These are group of substances with greasy consistency. They are with long hydrocarbon chain containing carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. In lipids, hydrogen to oxygen ratio is greater than 2:1. Lipid is a broader term used for fatty acids and their derivatives. They are soluble in organic solvents (non-polar solvents).
Fatty acids are organic acids which are composed of hydrocarbon chain ending in carboxyl group (-COOH). They can be:-
–Saturated fatty acids
–Unsaturated fatty acids
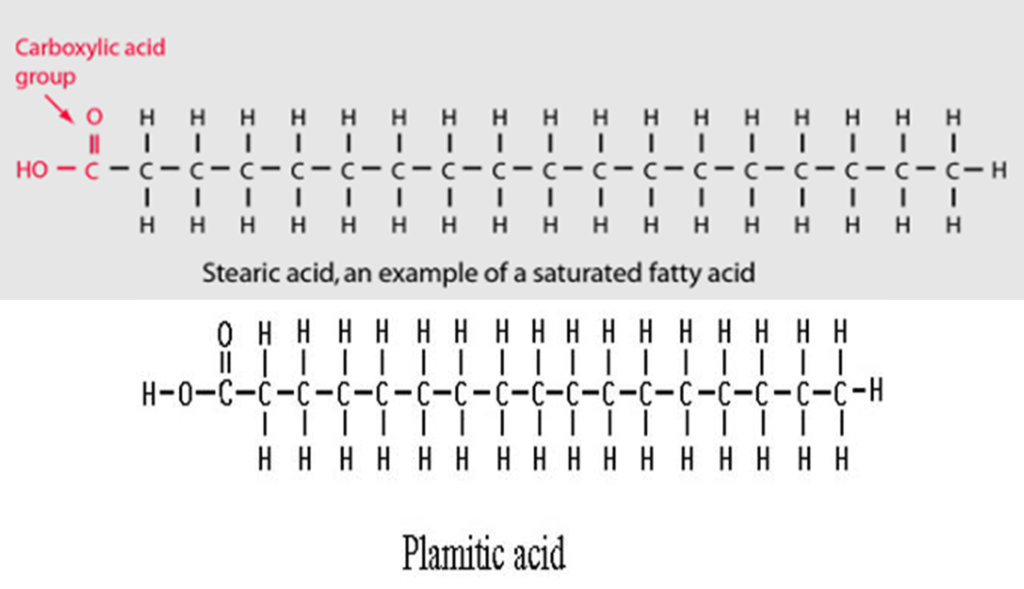
Saturated fatty acids:
They are with no double bonds between the carbon atoms of the hydrocarbon chain. e.g.
•Palmitic (C16H32O2) and
•stearic acids (C18H36O2)
–found in all animal and plant fats
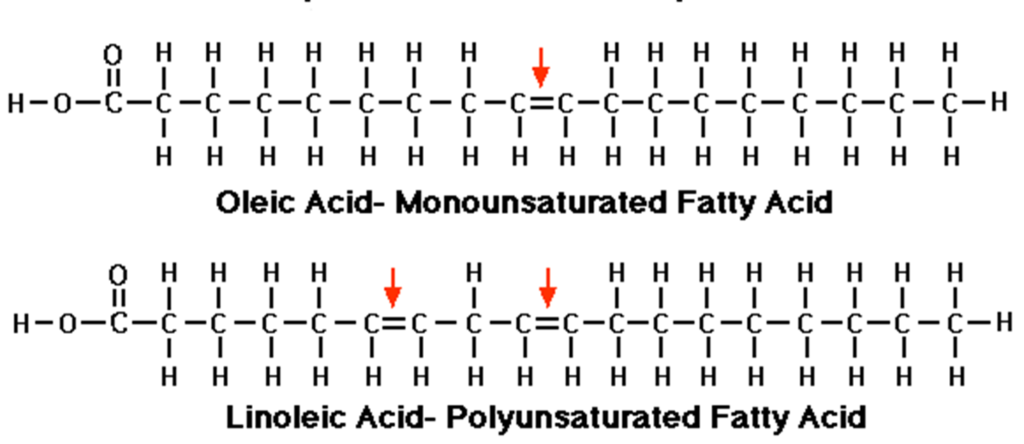
Unsaturated Fatty Acids:
They are with one or more double bonds between the carbon atoms of the hydrocarbon chain.e.g.
•Oleic acid (C18H34O2) found in nearly all fats and
•Linoleic acid (C18H32O2) found in many seed oils
These fatty acids are basic molecules which form different kinds of lipids. Lipids may be classified as-simple, compound and derived lipids.
Simple Lipids:
These are esters of fatty acids with various alcohols.
–Fats and waxes are simple lipids.
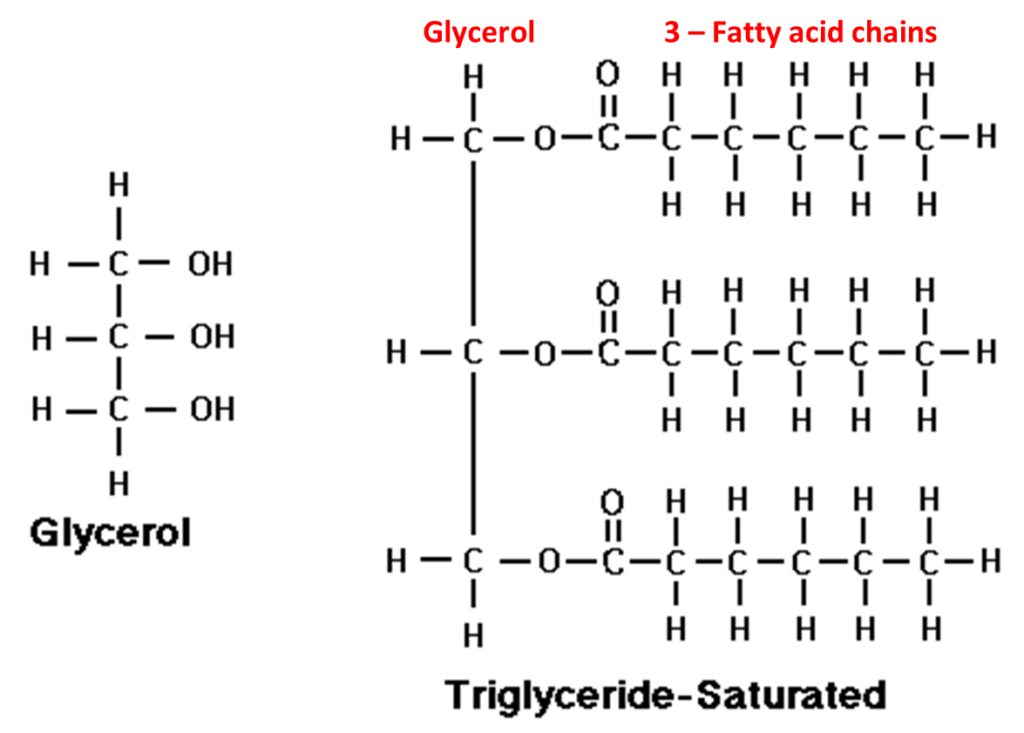
–Fats:
•Fats are esters of fatty acids with glycerol (CH2OH-CHOH-CH2OH).
Triglycerides are three molecules of fatty acids and one molecule of glycerol.
Generally, unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature and are called oils.
Unsaturated fatty acids are hydrogenated to produce fats
–e.g. Vanaspati ghee.
Fats are a nutritional source with high calorific value. Fats act as reserved food materials.
–In plants, it is stored in seeds to nourish embryo during germination.
–In animals fat is stored in the adipocytes of the adipose tissue.
Fats deposited in subcutaneous tissue act as an insulator and minimize loss of body heat. Fats deposited around the internal organs act as cushions to absorb mechanical shocks.
Wax
•It is another example of simple lipid.
•They are esters of long chain fatty acids with long chain alcohols.
•They are most abundant in the blood, the gonads and the sebaceous glands of the skin.
•Waxes are not as readily hydrolysed as fats.
•They are solid at ordinary temperature.
•Waxes form water insoluble coating on
–hair and skin in animals,
–waxes form an outer coating on stems, leaves and fruits.

Compound lipids :
–These are ester of fatty acids containing other groups like phosphate (Phospholipids), sugar (glycolipids), etc.
–They contain a molecule of glycerol, two molecules of fatty acids and a phosphate group or simple sugar.
–Some phospholipids such as lecithin also have a nitrogenous compound attached to the phosphate group.
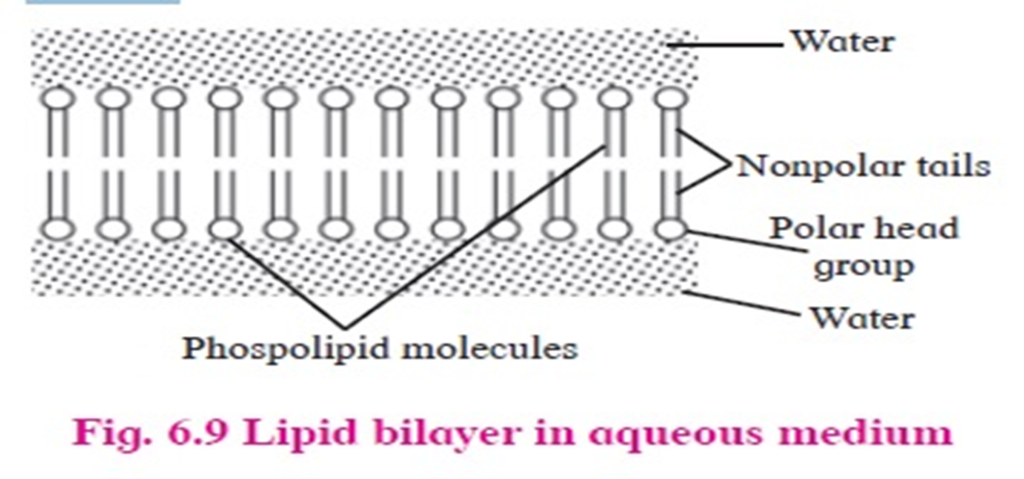
–Phospholipids:
•have both hydrophilic polar groups (phosphate and nitrogenous group) and hydrophobic non-polar groups (hydrocarbon chains of fatty acids).
•Phospholipids contribute in the formation of cell membrane.
–Glycolipids :
•contain glycerol, fatty acids, simple sugars such as galactose and nitrogenous base.
•They are also called cerebrosides.
•Large amounts of them have been found in the brain white matter and myelin sheath.
Derived Lipids:
–Sterols :
•They are derived lipids.
•They are composed of fused hydrocarbon rings (steroid nucleus) and a long hydrocarbon side chain.
•One of the most common sterol is cholesterol.
•It is widely distributed in all cells of the animal body, but particularly in nervous tissue.
•Cholesterol exists either free or as cholesterol ester.
•Adrenocorticoids, sex hormones (progesterone, testosterone) and vitamin D are synthesized from cholesterol.
•Cholesterol is not found in plants.
•In plants, sterols exist chiefly as Phytosterols.
•Yam Plant (Dioscorea) produces a steroid compound called diosgenin.
–It is used in the manufacture of antifertility pills. i.e. birth control pills.